थॅलेसेमिया म्हणजे काय? संपूर्ण माहिती – कारण, लक्षणे, उपचार आणि प्रतिबंध
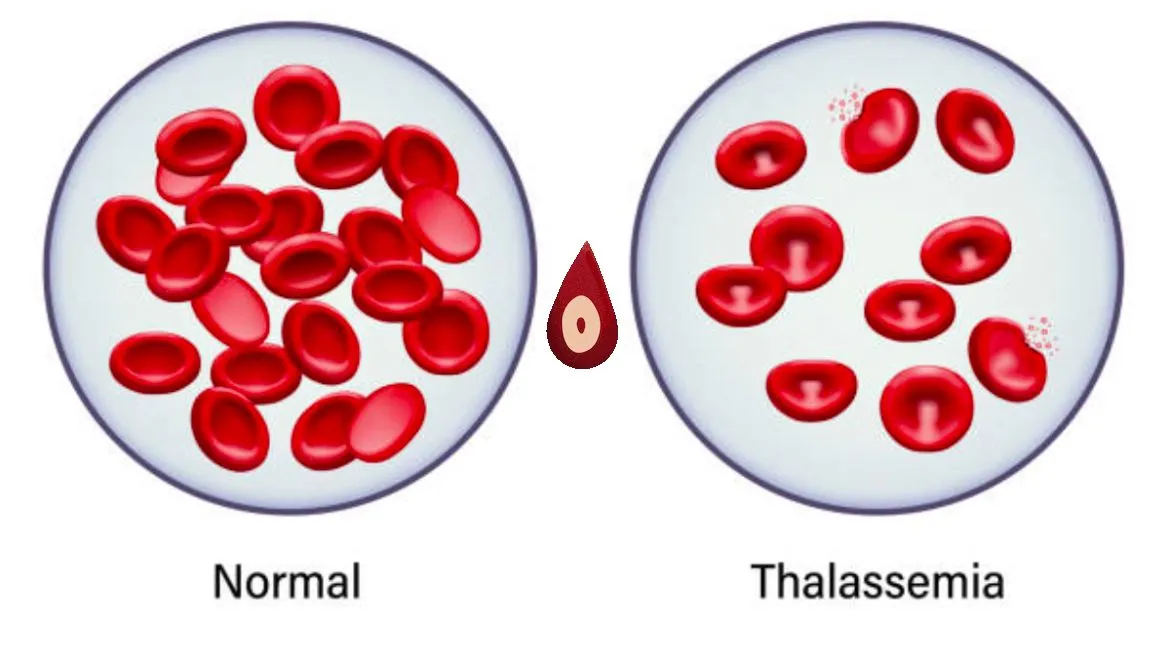
थॅलेसेमिया हा एक अनुवांशिक (Genetic) रक्तविकार आहे ज्यात शरीर पुरेसं हिमोग्लोबिन (Hemoglobin) तयार करू शकत नाही. हिमोग्लोबिन हे रक्तातील प्रथिन आहे जे ऑक्सिजन शरीरभर पोहोचवते. थॅलेसेमियामुळे शरीरात रक्ताची कमतरता (अॅनिमिया) निर्माण होते, थकवा, पांढरटपणा आणि इतर अनेक आरोग्य समस्या दिसतात.
भारतामध्ये दरवर्षी सुमारे १०,००० हून अधिक बालकं थॅलेसेमियासह जन्म घेतात, आणि लाखो लोक ‘कॅरिअर’ आहेत — म्हणजेच त्यांच्या शरीरात हा जीन दोष आहे पण लक्षणे नसतात. योग्य तपासणी आणि जनजागृतीने हा आजार पूर्णतः टाळता येऊ शकतो.
थॅलेसेमियाचे प्रकार
थॅलेसेमियाचे दोन प्रमुख प्रकार असतात:
-
थॅलेसेमिया मायनर (Thalassemia Minor / Carrier):
या प्रकारात व्यक्तीला हलका अॅनिमिया असतो किंवा काहीच लक्षणे नसतात. पण जर दोन्ही पती-पत्नी मायनर असतील तर त्यांच्या अपत्याला गंभीर थॅलेसेमिया होऊ शकतो. -
थॅलेसेमिया मेजर (Thalassemia Major):
हा गंभीर प्रकार आहे. यात बाळाच्या शरीरात हिमोग्लोबिन तयार होत नाही आणि जन्मानंतर ६ महिन्यांपासून गंभीर अॅनिमिया सुरू होतो. या रुग्णांना आयुष्यभर नियमित ब्लड ट्रान्सफ्यूजन आणि औषधोपचार करावे लागतात.
कारण
थॅलेसेमिया हा पालकांकडून मिळालेला जीन दोष आहे.
जर दोघांनाही हा दोष असेल (दोघेही Carrier असतील), तर अपत्याला थॅलेसेमिया मेजर होण्याची २५% शक्यता असते. त्यामुळे विवाहापूर्वी रक्ताची तपासणी करून कॅरिअर स्टेटस जाणून घेणे अत्यावश्यक आहे.
लक्षणे
थॅलेसेमिया मेजर असलेल्या रुग्णांमध्ये खालील लक्षणे दिसू शकतात:
-
सतत थकवा, कमजोरी
-
त्वचा आणि ओठ पांढरट दिसणे
-
श्वास घेण्यास त्रास
-
वजन न वाढणे, वाढ खुंटणे
-
पोट फुगणे (प्लीहा व यकृत वाढणे)
-
हाडांच्या रचनेत बदल
-
वारंवार ताप किंवा संसर्ग
थॅलेसेमिया मायनर असलेल्या व्यक्तींना सामान्यतः ही लक्षणे दिसत नाहीत.
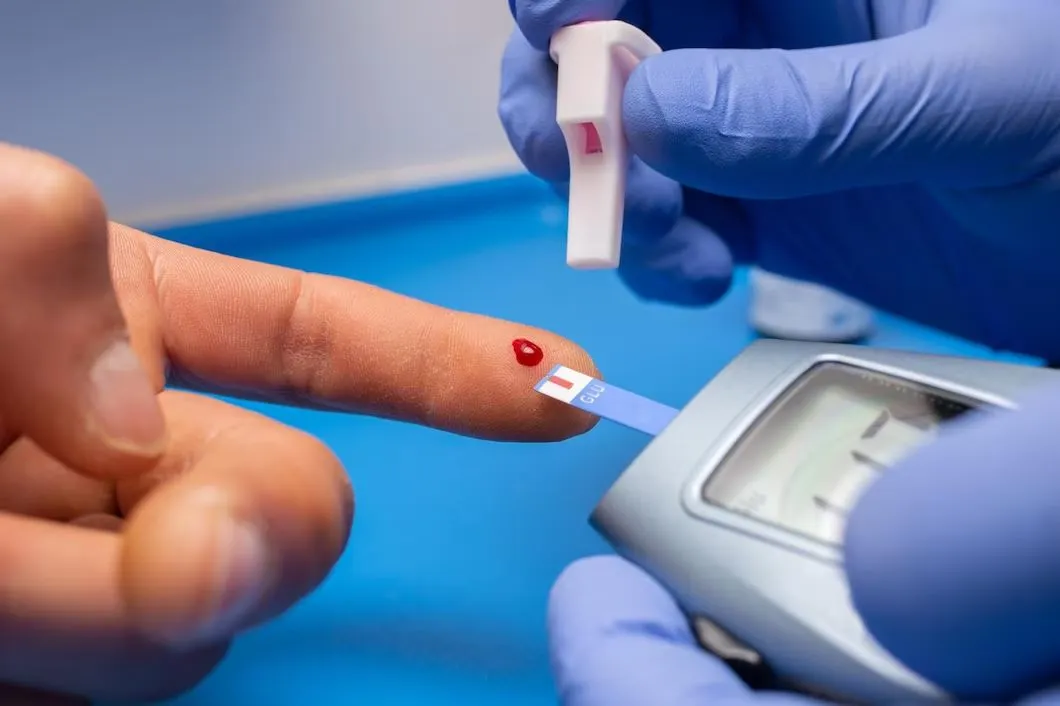
निदान कसे होते?
थॅलेसेमियाचे निदान सोप्या रक्तचाचणीने करता येते:
-
CBC (Complete Blood Count) – हिमोग्लोबिन व पेशींचा आकार तपासण्यासाठी
-
हिमोग्लोबिन इलेक्ट्रोफोरेसिस – थॅलेसेमिया प्रकार ओळखण्यासाठी
-
DNA चाचणी – अचूक जीन दोष शोधण्यासाठी
ही चाचणी लग्नाआधी किंवा गर्भधारणेपूर्वी करणे सर्वात सुरक्षित उपाय आहे.
उपचार
सध्या थॅलेसेमियासाठी खालील उपचार पद्धती वापरल्या जातात:
-
नियमित रक्तपरिवहन (Blood Transfusion):
गंभीर रुग्णांना दर ३–४ आठवड्यांनी रक्त चढवावे लागते. यामुळे हिमोग्लोबिनचे प्रमाण टिकते. -
आयरन-चेलेशन थेरपी (Iron Chelation):
वारंवार रक्त दिल्याने शरीरात लोह जास्त साचते. ते कमी करण्यासाठी विशेष औषधोपचार (जसे deferasirox, deferoxamine) करावे लागतात. -
बोन मॅरो ट्रान्सप्लांट (Bone Marrow Transplant):
हा उपचार काही निवडक रुग्णांमध्ये एकदाच आणि कायमचा उपाय ठरतो. योग्य डोनर मिळाल्यास पूर्ण बरा होण्याची शक्यता असते. -
जीन थेरपी (Gene Therapy):
आधुनिक तंत्रज्ञानाद्वारे दोषी जीन दुरुस्त करून हिमोग्लोबिनची निर्मिती सुधारण्याचा प्रयत्न केला जातो. ही पद्धत अजून महाग आहे पण भविष्यात मोठी आशा आहे.
आहार आणि जीवनशैली
थॅलेसेमिया असलेल्या लोकांनी खालील गोष्टी पाळाव्यात:
-
डॉक्टरांच्या सल्ल्यानुसार नियमित तपासणी करावी
-
आयरनयुक्त सप्लिमेंट्स स्वतःहून घेऊ नयेत
-
जीवनसत्व C आणि प्रोटीनयुक्त अन्न जसे डाळी, अंडी, फळे-भाज्या खाव्यात
-
हिपॅटायटिस, फ्लू, टायफॉइड यांसारख्या लसी वेळेवर घ्याव्यात
-
पुरेशी झोप, हलका व्यायाम, आणि तणावमुक्त जीवनशैली ठेवावी
थॅलेसेमिया टाळण्याचे उपाय
थॅलेसेमिया पूर्णपणे रोखता येऊ शकतो, जर आपण योग्य वेळी खबरदारी घेतली तर:
-
लग्नापूर्वी थॅलेसेमिया चाचणी करणे
-
दोघेही Carrier असल्यास जीन काउन्सिलिंग करणे
-
गर्भधारणेदरम्यान प्री-नॅटल चाचणी (Prenatal Test) करून गर्भातील आजार तपासणे
-
शाळा, महाविद्यालय, आणि समाजात जनजागृती करणे
-
रक्तदान शिबिरे आणि थॅलेसेमिया केंद्रांना सहकार्य करणे
सरकार आणि समाजाची भूमिका
भारत सरकारकडून थॅलेसेमिया नियंत्रणासाठी विविध उपक्रम सुरू आहेत –
-
राष्ट्रीय थॅलेसेमिया नियंत्रण कार्यक्रम
-
कॅरिअर स्क्रिनिंग शिबिरे
-
मोफत रक्तपरिवहन सेवा
-
औषधोपचारासाठी आर्थिक सहाय्य योजना
स्थानिक रुग्णालये, एनजीओ, आणि स्वयंसेवी संस्था यांनी जनजागृती वाढवणे हे अत्यंत आवश्यक आहे.
निष्कर्ष
थॅलेसेमिया हा केवळ वैद्यकीय नव्हे तर सामाजिक जबाबदारीचा विषय आहे.
एक साधी रक्तचाचणी — तुमचं आणि पुढच्या पिढीचं आयुष्य वाचवू शकते.
जाणकार व्हा, तपासणी करा आणि इतरांनाही जागरूक करा.
तुमच्यासाठी सल्ला
जर तुम्हाला थॅलेसेमिया तपासणी, जीन काउन्सिलिंग किंवा रक्तदान शिबिराबद्दल माहिती हवी असेल,
तर आपल्या जवळच्या सरकारी किंवा मान्यताप्राप्त आरोग्य केंद्राशी संपर्क साधा.
???? “थॅलेसेमिया मुक्त भारत” हा तुमच्या एका निर्णयावर अवलंबून आहे!
संदर्भ (Sources):
-
भारतीय आरोग्य मंत्रालय – Thalassemia Control & Prevention Guidelines
-
WHO: Thalassemia Management & Genetic Counseling Framework
-
Indian Journal of Hematology & Blood Transfusion (2024 Review)
-
Thalassemia International Federation Reports
IN ENGLISH
Thalassemia: A Preventable Genetic Blood Disorder
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder in which the body is unable to produce enough hemoglobin — the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body.
Due to this deficiency, anemia, fatigue, paleness, and other health problems occur.
In India, more than 10,000 children are born with Thalassemia every year, and millions are carriers — meaning they carry the defective gene but show no symptoms.
With proper testing and awareness, this disorder can be completely prevented.
Types of Thalassemia
1. Thalassemia Minor (Carrier):
Individuals with this type have mild anemia or no symptoms at all.
However, if both partners are carriers, there is a high risk of their child being born with severe Thalassemia.
2. Thalassemia Major:
This is the severe form of the disease. The child’s body cannot produce hemoglobin properly, and severe anemia develops within the first six months of life.
These patients require lifelong blood transfusions and medications.
Cause
Thalassemia is caused by a genetic defect inherited from parents.
If both parents are carriers, there is a 25% chance that their child will have Thalassemia Major.
Hence, pre-marital blood screening to determine carrier status is crucial.
Symptoms
Common symptoms in Thalassemia Major patients include:
-
Constant fatigue and weakness
-
Pale skin and lips
-
Shortness of breath
-
Poor weight gain or stunted growth
-
Abdominal swelling (due to enlarged spleen and liver)
-
Bone deformities
-
Frequent fever or infections
People with Thalassemia Minor usually do not show these symptoms.
Diagnosis
Thalassemia can be detected through simple blood tests, such as:
-
CBC (Complete Blood Count): To check hemoglobin levels and red blood cell size.
-
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis: To identify the specific type of Thalassemia.
-
DNA Test: To detect the exact genetic mutation.
It is highly recommended to perform these tests before marriage or pregnancy.
Treatment Options
Currently, Thalassemia is managed through the following medical approaches:
1. Regular Blood Transfusions:
Severe patients require transfusions every 3–4 weeks to maintain hemoglobin levels.
2. Iron Chelation Therapy:
Frequent transfusions cause excess iron buildup in the body. Special medications (like Deferasirox or Deferoxamine) help remove it.
3. Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT):
In some selected cases, a successful BMT can completely cure the disease — provided a suitable donor is available.
4. Gene Therapy:
This advanced technique aims to correct the faulty gene and restore hemoglobin production.
Though still expensive, it offers great hope for the future.
Diet and Lifestyle Guidelines
People with Thalassemia should follow these essential health tips:
-
Regular medical check-ups as advised by doctors
-
Avoid taking iron supplements without medical supervision
-
Eat foods rich in vitamin C and proteins (like pulses, eggs, fruits, and vegetables)
-
Take timely vaccinations (Hepatitis, Flu, Typhoid, etc.)
-
Maintain proper sleep, light exercise, and a stress-free lifestyle
Prevention: The Most Powerful Cure
Thalassemia can be completely prevented if the right steps are taken in time:
-
Get Thalassemia screening before marriage
-
If both are carriers, seek genetic counseling
-
During pregnancy, undergo prenatal testing to detect any fetal disorder
-
Conduct awareness programs in schools, colleges, and communities
-
Support blood donation drives and Thalassemia care centers
Role of Government and Society
The Government of India has launched several initiatives to control Thalassemia, such as:
-
National Thalassemia Control Program
-
Carrier Screening Camps
-
Free Blood Transfusion Services
-
Financial Assistance Schemes for Treatment
Hospitals, NGOs, and community organizations must actively participate in spreading awareness.
Conclusion
Thalassemia is not just a medical issue, but a social responsibility.
A simple blood test can save your life — and the lives of future generations.
Be informed. Get tested. Spread awareness.
“A Thalassemia-Free India depends on just one decision — yours.”
If You Need Help
For information about Thalassemia testing, genetic counseling, or blood donation camps,
contact your nearest government or authorized health center.
References:
-
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India – Thalassemia Control & Prevention Guidelines
-
World Health Organization (WHO): Thalassemia Management & Genetic Counseling Framework
-
Indian Journal of Hematology & Blood Transfusion (2024 Review)
-
Thalassemia International Federation Reports
संबंधित पोस्ट
वेबसाइट पोल
विशेष:
आम्हाला फॉलो करा
सब्सक्राइब करा न्यूज़लेटर
SUBSCRIBE US TO GET NEWS IN MAILBOX
वेअथेर रिपोर्ट
लाइव क्रिकेट स्कोर
शेअर मार्केट
Ticker Tape by TradingView
Stock Market by TradingView
© 2026 The Global Times | Powered By by Sysmarche Infotech







































रिपोर्टर
With an MBA in Marketing (First Class with Distinction) and a deep passion for business strategy and innovation, I aim to bring new ideas to life through clarity, creativity, and strong leadership. As the Director of The Global Times, I focus on driving growth, building meaningful collaborations, and creating opportunities that make an impact. My vision is to take our brand to global heights — through digital innovation, smart planning, and ethical business practices. I’m constantly learning, evolving, and planning to pursue my PhD further — because growth never stops.
Krutika Tushar KhanvilkarDedicated to empowering teams, inspiring people, and setting new standards of excellence in the industry.